Qualitative determination of compositions, morphologies and associations/distributions of fluid inclusions/fluid inclusion assemblages is undertaken during routine petrographic studies (and illustrated by photomicrography).
Using specialised equipment, heating and freezing of fluid inclusions provides a basis for calculation & estimation of fluid composition (salinity), and temperatures of fluid entrapment.
Gas Chromatography and Ramon Spectroscopy may also be applied to fluid inclusion composition determination.
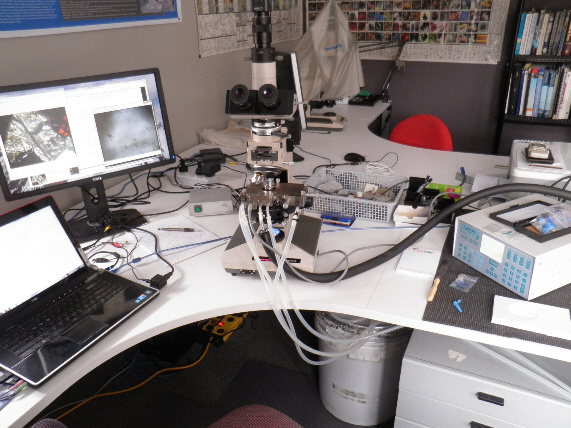
Left. APSAR fluid inclusion microthermometry set-up using INSTEC HCS622GXY heating stage and mk1000 temperature controller.


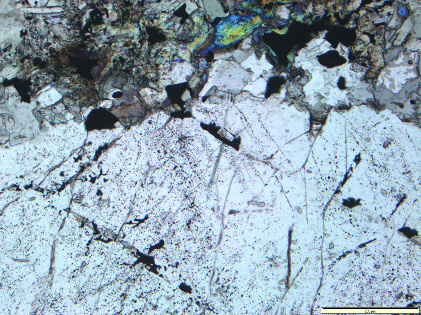
Above. Polyphase fluid inclusions in granoblastic quartz of porphyry/magmatic hydrothermal style veining. Inclusion compositions include: (left) aqueous liquid, carbonic liquid and gas, chalcopyite and unresolvable translucent mineral; and (right) aqueous liquid and vapour, hematite, halite and unresolvable opaque mineral.
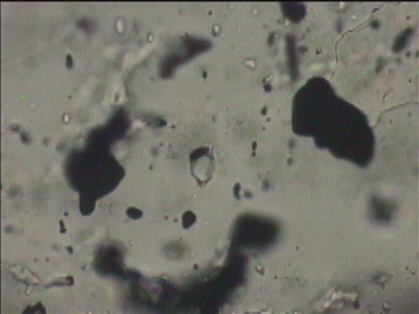
Below Left. Multiple stage fluid inclusion assemblages in brittle deformed to partly recrystallised apatite of metamorphic- style veining of orogenic/intrusion-related ore system: Early secondary/peudosecondary hypersaline carbonic aqueous fluid inclusion assemblages overprinted by later/younger liquid-rich aqueous fluid inclusion assemblages, the latter contained along discrete annealed microfractures microstructurally continuous with carbonate, native gold and epidote veining. Below right. Youngest aqueous fluid inclusions enclosing grains if native gold and carbonate.
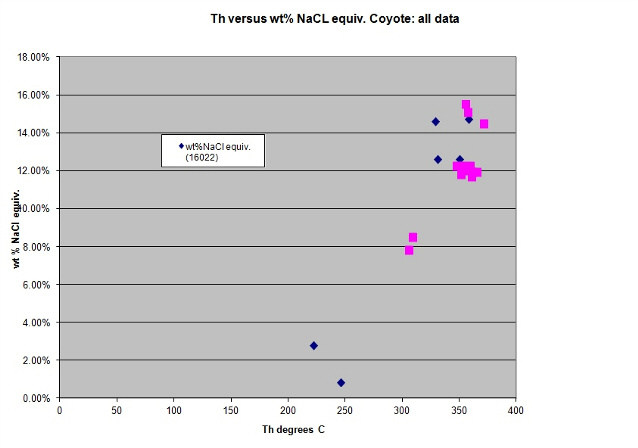
Representation of fluid inclusion heating and freezing data: Fluid inclusion H2O homogenisation temperatures versus NaCl wt% (calculated from measured H2O melting temperatures).
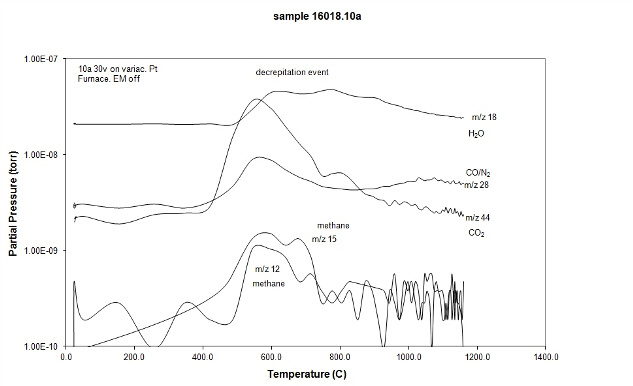
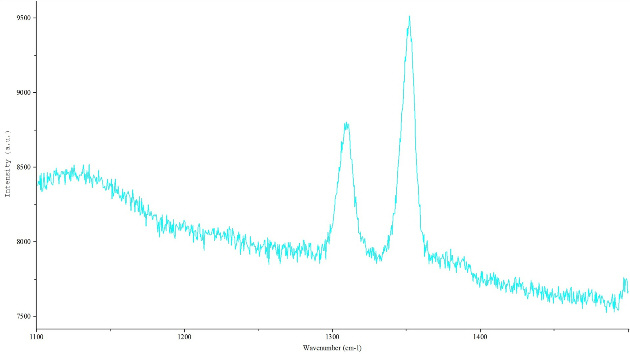
Gas chromatographic spectra of decrepitated fluid inclusion assemblage indicating the presence of nitrogen, methane and carbonic gases together with aqueous fluid. ..
Ramon spectra of individual fluid inclusion identifying the presence of methane gas. .